Part 0: Diversity
Table of Contents

What is Diversity?
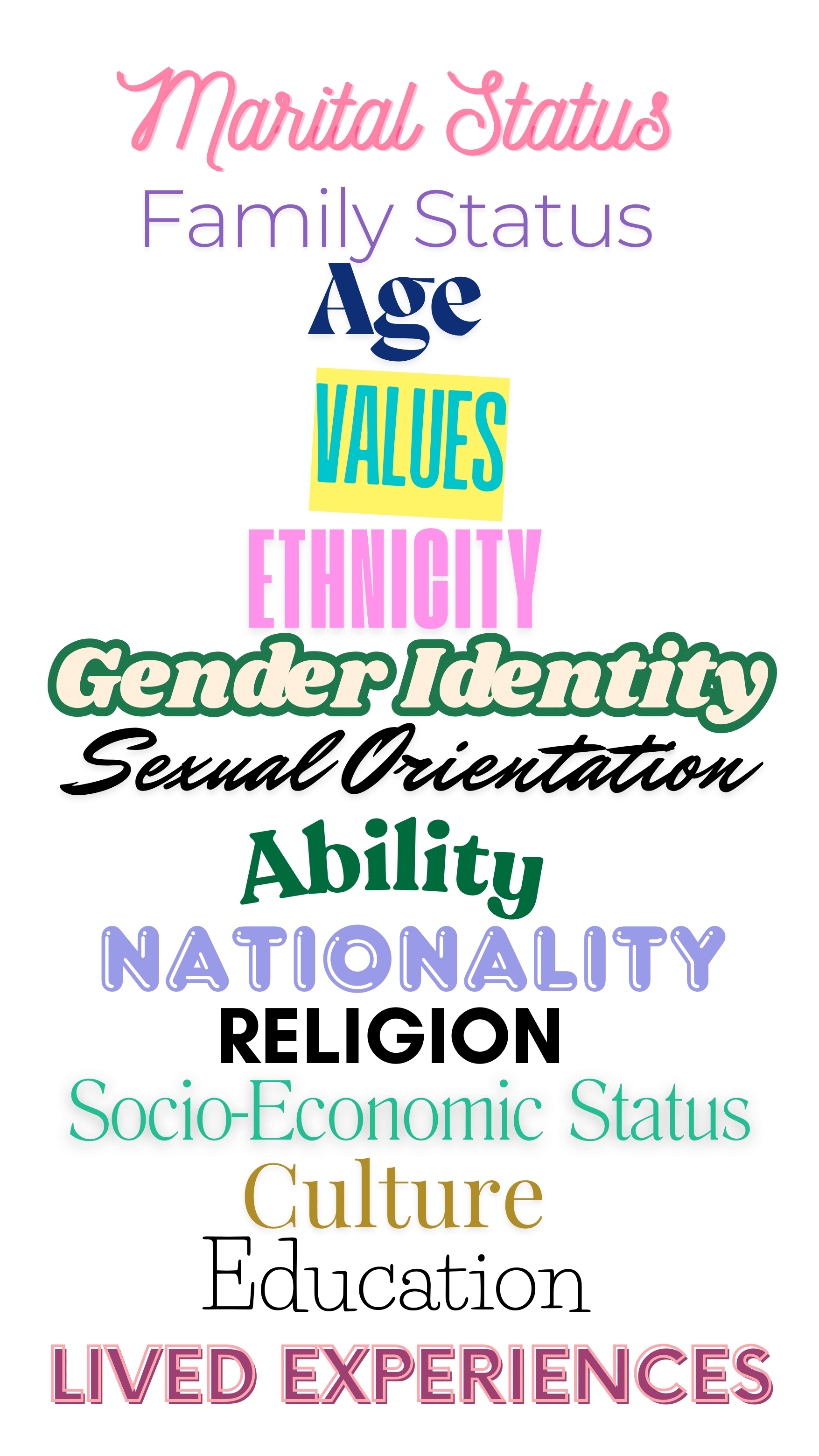
Diversity acknowledges and involves the differences among people. This includes but is not limited to, characteristics such as:
Marital Status – An individual’s relationship status.
Family Status – An individual’s relationship with their family of origin and/or their chosen family.
Age – The length of time an individual has been alive.
Values – Fundamental beliefs that guide or motivate attitudes or actions.
Ethnicity – A group of people who identify with each other based on perceived shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups.
Gender Identity – The personal sense of one’s gender.
Sexual Orientation – The gender to which a person is attracted.
Ability – The quality of having the means or skill to do something.
Nationality – The legal status of belonging to a particular country.
Religion – A particular system of faith and worship.
Socio-Economic Status – The differences between groups of people caused mainly by their financial situation.
Culture – The values and beliefs, language, communication, and practices shared by a group.
Education Status – The level of education completed by an individual.
Lived Experiences – Episodes in one’s life that have shaped one’s worldview, problem-solving approach, or leadership qualities.